Hair care products, as essential products for damaged hair such as permed and dyed hair, always have a place in the market. The performance of hair care products largely depends on the choice of cationic conditioning agents. In this issue, let's talk about the formula composition of hair conditioner and how to choose cationic conditioning agents.
Hair Conditioner with Cationic Ingredients
Hair conditioner is a specialized product for use after shampooing, divided into leave-in conditioner and rinse-out conditioner depending on the method of use. It can neutralize molecules with anionic residues remaining on the hair surface, forming a monolayer film, closing the hair cuticles, making tangled hair smooth, easy to comb, and has the effect of conditioning the hair.
Hair conditioner is generally an O/W system, mainly composed of cationic surface active agent, fatty alcohols, thickeners, preservatives, colorants, fragrances, and other active ingredients. Fatty alcohols mainly thicken and whiten cationic emulsifiers; cationic conditioning agents can soften, anti-static, moisturize, and condition the hair; thickeners such as lanolin, olive oil, silicone oil, etc., can improve the nutritional status of the hair in the conditioner, making the hair shiny, easy to comb; other active ingredients such as anti-dandruff agents, wetting agents, sunscreens, hydrolyzed proteins, plant extracts, etc., give various functions to the conditioner.
Common Conditioning Agents In Hair Conditioner with Cationic Ingredients
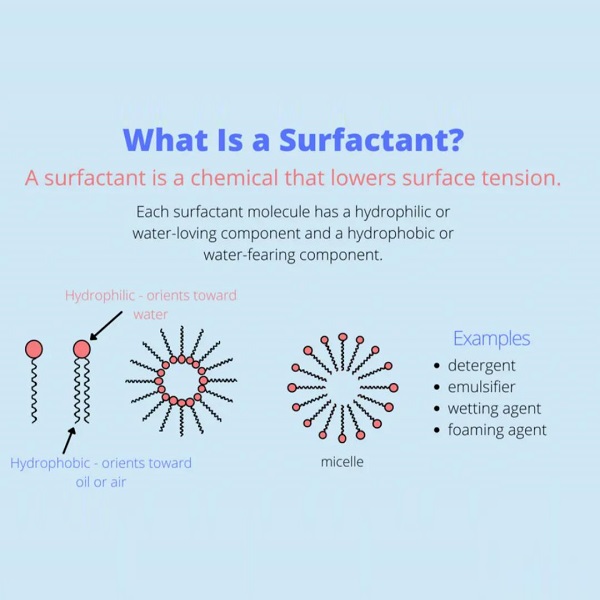
Hair conditioners use cationic surface active agent, which is usually quaternary ammonium surfactants, consisting of an ammonium cation [H4N+] with four hydrogen atoms fully substituted by organic groups. Quaternary ammonium salts contain long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains and polar positively charged ends. After ionization in water, they combine with the negative charges in the hair protein structure through ionic electrostatic attraction, retaining the hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains on the hair surface together, making the hair surface smooth, lubricated, soft, and easy to comb. The conductivity of quaternary ammonium salts can reduce the accumulation of static electricity in the hair, reduce hair fluttering, and improve combing performance.
Common Types of Cationic Conditioning Agents Include
Behentrimonium Chloride(KDMP/BT85/2231): Has excellent wet/dry feel and combing properties, good anti-static effect, significantly improves the dry/wet combing and softness of the hair, enhances hair shine and anti-static ability, especially suitable for hair care products for damaged hair such as coloring and perming.
Behentrimonium Methosulfate(BTMS): Has outstanding anti-tangling ability on hair, does not accumulate on the hair, moisturizes and strengthens the hair, making it smooth, silky.
MONSA® BTMS -50/90
INCI name | Behentrimonium Methosulfate |
Trade name | MONSA® BTMS-50/90 |
CAS No. | 81646-13-1 |
Molecular formula | C26H57NO4S |
Dosage | 0.10~10% |
Packaging | 20kg/paper drum |
Trimethylstearylammonium Chloride (OTAC/STAC/1831): An ammonium chloride with an octadecyltrimethyl structure, possessing excellent properties of penetration, softening, antistatic, and antimicrobial effects, providing certain conditioning and antistatic properties to the hair.
Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Chloride (CTAC/1631): An ammonium chloride with a hexadecyltrimethyl structure, notable for its enhancement of hair softness and outstanding antistatic properties, commonly used as a hair conditioning agent to improve various hair characteristics, typically added at 1%-2%.
Stearamidopropyl Dimethylamine (SPA/S18): Offers good conditioning properties to the hair, improves both wet and dry combing performance, moderately deposits on the hair, effectively controlling hair volume, particularly suitable for daily care of hair ranging from undamaged to damaged.
Behenamidopropyl Dimethylamine (BD22/BAP): Balancing non-ionic and cationic properties, it exhibits good compatibility with anionic surfactants. It can be used in cream-based hair care products and hair repair products, concentrating on repairing hair quality, with excellent reparative effects on damaged hair.
The performance of hair conditioners is related to the carbon chain length of quaternary ammonium salt hydrophobic chains: as the carbon chain length increases, the water solubility of alkyl quaternary ammonium salt cations decreases, leading to increased thickening and conditioning performance. Longer carbon chains such as C12-C22 exhibit better conditioning effects compared to chains with fewer than 12 carbon atoms. Under the same carbon chain conditions, the antistatic ability of dimethylamine-type cations is weaker than that of alkyl-type cationic conditioners, with better volume performance after drying.